Infection Management
with Diagnostics
Outpace Infections: Empowering Physicians to
Deliver Timely, Accurate Care
Respiratory tract infection
is a leading cause of visits
to the Emergency Department (ED).
www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb277-Top-ReasonsHospital-Stays-2018.pdf

Infection Management in Immunodiagnostics
Infection Management, also referred to as Infection Prevention and Control, is a practice within healthcare settings aimed at minimizing the risk of transmitting infections by implementing procedures to prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms among patients, healthcare workers, and visitors, often including practices like hand hygiene, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and safe handling of medical waste.
Diagnostics Role in Infection Management
Diagnostics play an important role in infection control in hospitals by accurately identifying the specific pathogens causing infections, guiding targeted treatment, enabling the implementation of appropriate infection control measures, and providing effective surveillance to monitor outbreaks and track antimicrobial resistance patterns. Ultimately diagnostics can improve patient care while helping to minimize the spread of infections within the healthcare setting.
The area in a hospital where it is generally considered most difficult to minimize the spread of infections is the Emergency Department (ED), due to the high volume of patients with unknown infectious statuses, rapid patient turnover, and often crowded conditions.
A crucial first step in designing
a treatment plan and minimizing the transmission of infection
is determining whether an infection is bacterial or viral.
Bacterial vs Viral Infections: Key to Effective Treatment
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s immune system has an extreme response to an infection or injury. It can progress quickly and unpredictably, leading to organ failure, shock, and sometimes death. Sepsis is caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, with bacteria being the most common cause.
Symptoms of Sepsis include:
- Fever or low body temperature
- Chills
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Skin rash
- Confusion and disorientation
- Light headedness

For more information, please visit Sepsis Alliance
250,000
deaths because of sepsis in the U.S. Annually among all hospital deaths1
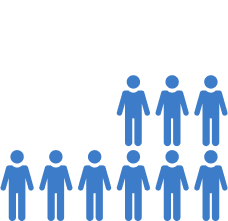
50%
Sepsis-related deaths among all hospital deaths2
1 Fleischmann C, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 193: 259e72.
2 Statistical Brief #225. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). June 2017. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
Navigating the challenges of acute infections
in emergency departments
The Emergency Department (ED) is often a fast-paced and high-pressure environment. When a patient presents with signs of an acute infection, it’s easy to feel like you’re juggling multiple tasks at once. Diagnostic uncertainty is constant, and the fear of missing something critical is ever-present. With every decision needing to be made swiftly, time feels like a luxury we don’t have.
Bacterial and viral infections are clinically indistinguishable, physicians are faced with significant clinical uncertainty1.
1 MeMed survey of ED pediatricians (n=42). 2. D Wang, et al.
Primary Care Respiratory Medicine (2021).
>40%
Antibiotic
overuse rates
20%
Antibiotic
underuse rates
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the top
global public health and development threats
HEALTH IMPACT1
4.95 Million
DEATHS ASSOCIATED TO
BACTERIAL AMR
1.27 Million
DEATHS ATTRIBUTABLE
TO BACTERIAL AMR
1Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis.
ECONOMIC IMPACT2
US $ 1 Trillion
ADDITIONAL HEALTHCARE
COSTS BY 2050
US $ 1 - 3.4 Trillion
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP)
LOSSES PER YEAR BY 2030
2Drug-Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic future (March 2017).
Patient Care and Satisfaction
On top of these clinical pressures, there's the constant focus on patient satisfaction and engagement. The fast pace of the ED can
sometimes make it feel like there’s a disconnect between the level of care you want to provide and the time constraints you’re under. But
every decision made in the ED doesn’t just affect immediate care — it has long-lasting effects on patient outcomes.

Patient impacts
Diagnostic uncertainty may affect patients in many ways:
- Decreasing patient satisfaction
- Confidence and trust in the providers and medical system
- Anxiety and stress
- Negative treatment response and side effects
- Increase costs of medical care

System impacts
When a patient presents to the ED with signs of an acute infection, current diagnostics and protocols may affect systems in many ways:
- Blood cultures may delay diagnosis and increase the risk of contamination.
- Pathogen panels can drive up healthcare costs and limit diagnostic coverage.
- Negative test results leave providers without clear next steps, stalling effective treatment.
- These inefficiencies strain healthcare resources and undermine patient outcomes by:
- Fueling inappropriate antibiotic use
- Accelerating antibiotic resistance
- Delaying critical interventions and contributing to Boarding patients in the ED
- Increasing risks of organ damage, sepsis, and potentially death
Diagnostic Stewardship
Diagnostic stewardship is a set of actions that improve the use of diagnostic tests to help patients receive the right care at the right time. The goal is to reduce the number of misdiagnoses and improve patient outcomes. Diagnostic stewardship is important across all phases of the diagnostic pathway, including pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical. It is a collaborative effort that requires building and sustaining partnerships between laboratory professionals, clinical care teams, and other experts.
The Goal of Diagnostic Stewardship is to reduce the number of misdiagnoses and improve patient care

